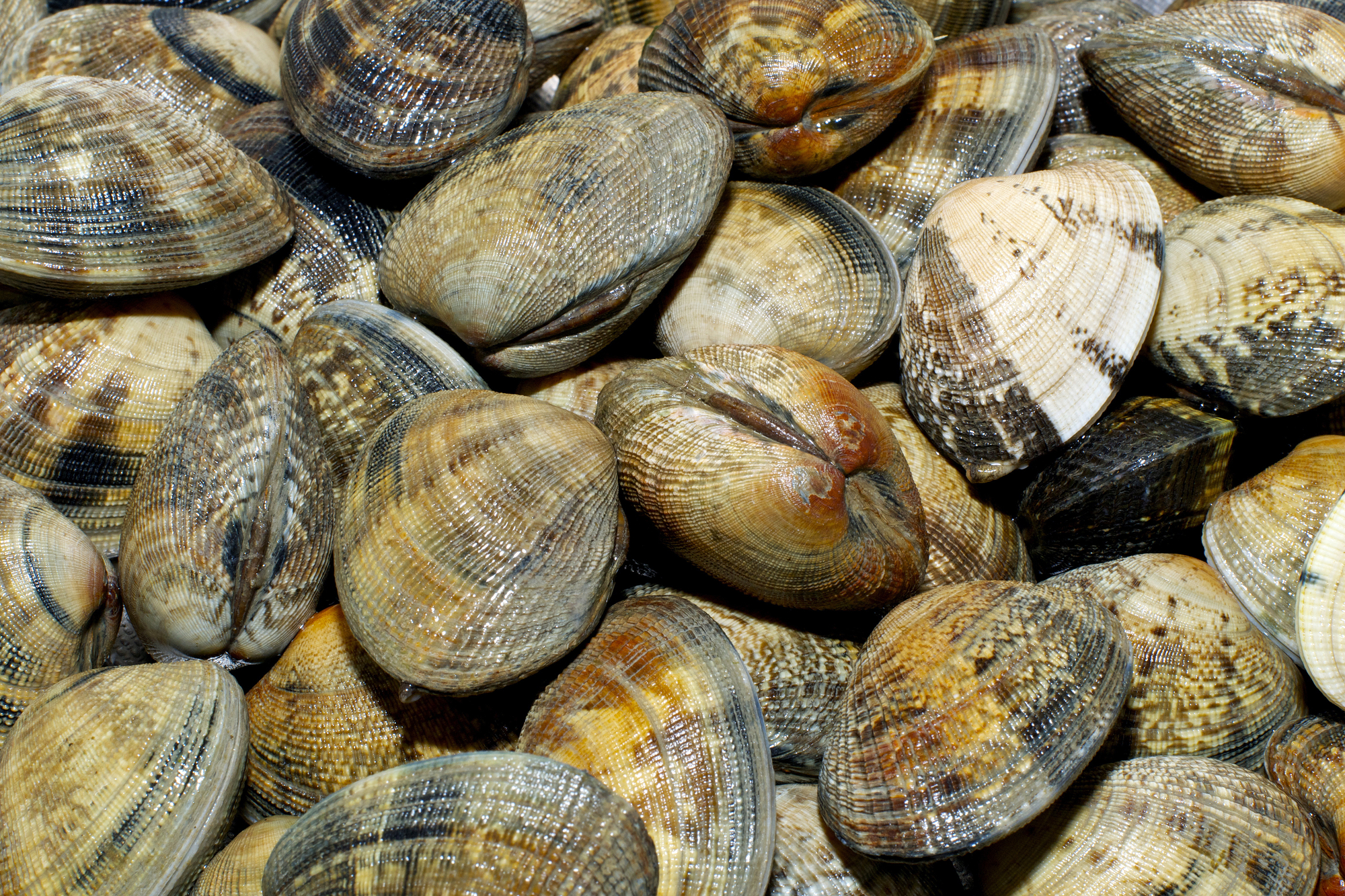
Thinking of making your own creamy clam chowder, savory clams casino, or chilled littlenecks served on the half-shell? Here’s some good news. All those dishes can begin the same way – with fresh quahogs plucked from Yarmouth’s coastal waterways.

Hard-shell clams or quahogs (pronounced KO-hogs), are found throughout the town’s saltwater bays and estuaries. To harvest them, you’ll need a recreational shellfishing permit, which can be purchased from Town Hall. You’ll also need to follow the local shellfishing rules, advises Yarmouth’s Director of Natural Resources Karl von Hone. Here are some of the basics:
- Yarmouth residents pay $30 for a one-year recreational license that covers quahogs, soft-shell clams (steamers), and sea clams, along with oysters and bay scallops, which have shorter seasons beginning in the fall. The permit price for non-residents is $80, and senior citizens (75 or older) pay $15.
- Quahogging and clamming season runs year-round in Yarmouth, beginning in April and ending the following March. But areas are subject to temporary closures during summer months – especially after heavy rains, when water quality sometimes drops below state safety standards for shellfishing. The town’s waters are tested regularly for bacteria concentrations under supervision of the Mass. Division of Marine Fisheries, von Hone said.
- Summer shellfishing in Yarmouth is limited to Sundays only. But during colder months, when weather is more likely to be inclement, Wednesdays are added.
- Family members can work together under a single recreational permit, raking in up to 10 quarts of quahogs and 10 quarts of soft shell clams per week.
- While Yarmouth has ample areas for quahogging, von Hone said that digging for soft shell clams (steamers) is limited.
- Quahogs must be at least 1 inch across the thickest part of the shell (near the hinged end), and soft shell clams must be at least 2 inches long. Local hardware shops and fishing tackle stores often sell gauges for measuring shellfish.
- Find complete information on Yarmouth’s shellfishing rules at the Division of Natural Resources website.
Safe family activity for social distancing
During summer, when both the air and water are comfortably warm, quahogging makes a great family outing, van Hone said. Think of swimming in the ocean for a couple of hours, and then returning home with your dinner.

It’s also a workable activity for social distancing under COVID-19 protocols. You’re outdoors in nature – often with a stiff ocean breeze in your face – and there’s generally room in the water to keep a safe distance from others. But you should still exercise caution when using limited parking areas or walking on paths to and from your destination. Be courteous and stop to allow others to pass with ample space, von Hone said. Since parking is limited at many of the popular shellfishing locations, it might be a good idea to have someone drop you off and then pick you up when you’re finished.
What gear will you need?
Collecting a 10-quart limit of fresh quahogs takes an hour or two of moderate work – more like play really, as you slosh around in waist-deep water and stop every minute or so to drop a couple of shellfish into your floating basket. To make your basket float, squeeze it into an overinflated tire tube and tether it to your waistline so that it bobs along wherever you go. It’s also wise to keep a shellfish gauge tied to the handle of your basket.
Chest-high waders are a good idea when the water is cold, but swim trunks will suffice during summer months. The only other equipment you’ll need is a quahog rake, which is a strong, steel-headed rake with long tines to pull the shellfish from their muddy beds. Shellfish rakes have sturdy wooden handles and a metal basket behind the tines to catch the shellfish. Once you get the hang of working a shellfish rake, you’ll actually feel the difference between scratching quahogs and dragging up a pile of rocks.

If you don’t have a rake, try feeling around with your feet. As kids growing up on the Cape, we always waded out at low tide to where the water was roughly waist-deep. Then we crouched down low, so the water covered our shoulders and we felt the bottom with our feet. The bay water was always murky, so we wore an old pair of sneakers, just in case we bumped into a menacing blue crab. Today, water socks make sneakers obsolete, and lightweight gloves with rubberized palms can help allay the fears of being pinched by a startled crab.
Where can i go quahogging?
Yarmouth has plenty of sheltered waters for scratching quahogs, but the town opens and closes different areas in a rotational plan, working with the state Division of Marine Fisheries, von Hone said. That’s why it’s important to check the Yarmouth Division of Natural Resources website for information.

For example, winter-season quahogging is allowed off Wilbur Park in Bass River, but during summer the open area rotates to Lewis Bay or Lewis Pond, said von Hone. In the fall, the open area is switched to Mill Creek, which is off of Lewis Bay, he said. Next it returns to Wilbur Park or Bass Hole, and it later switches back to the summer location, von Hone explained.
Lewis Pond, which is typically a popular summertime area, will be closed this year, von Hone said, noting that quahogging will be allowed in a section of Lewis Bay (stretching roughly from the end of New Hampshire Avenue to the mouth of Mill Creek). Find updated shellfishing locations on the Yarmouth DNR website.
Managing quahogs stocks for the future
As the town opens and closes its quahogging areas, the Yarmouth Division of Natural Resources is working to make sure the shellfish population remains strong, von Hone said. Yarmouth and some other Cape Cod towns participate in the shellfish relay, a program that dredges quahogs from the Taunton River estuary, which is contaminated with excess fecal bacteria. The shellfish are transferred to cleaner waters, where they quickly purge the bacteria and become safe to consume, von Hone said.
Last year the Lewis Bay area was seeded with about 96,000 pounds of quahogs in varying sizes, von Hone said, noting that once the shellfish were introduced, the area was closed for a full year. The long closure provided more than enough time for quahogs to clean themselves, he said. And it gave them a chance to spawn and produce new stock.
Each female quahog can produce up to 5 million eggs during a spawning, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, which manages ocean fisheries.
Why do quahogs have so many names?

A quahog by any other name is still a quahog, but the species of bivalve mollusk known by scientists as Mercenaria mercenaria is certainly a creature with many aliases. Northern quahog is the popular name, quahog is a Native American name for clam, and following is a quick guide to the other terms related to the quahog’s size:
- Little necks are the smallest legal size for quahogs, measuring just over 1 inch across the thickest part of the shell (right above the hinge). Because they’re small and tender, littlenecks are preferred for raw bars, as well as for grilling inside the shell or serving whole over pasta.
- Middle necks are slightly larger than littlenecks (1¼ inches above the hinge). They’re especially good for raw bars, grilling in the shell, steamers and clams casino.
- Top necks are the next size larger (1½ inches above the hinge) and are used for raw bars, steaming, and in-the-shell grilling. They’re also the perfect size for clams casino.
- Cherrystones are larger still (2 inches wide above the hinge). They’re a little tougher than the smaller sizes, but they still can be eaten raw, steamed, grilled or used in clams casino. Cherrystones are also big enough to use for chowders or in baked-stuffed quahogs (aka “stuffies”).
- Chowders are the largest of quahogs, sometimes half-a-pound each. The meat is tough and the flavor is strong, so they are typically steamed, then diced up for chowders or cooked, minced and mixed with bread cubes, butter, spices and sausage, then baked in the shell for stuffed quahogs.
Andy Tomolonis is a nonfiction author, travel writer and multimedia journalist.